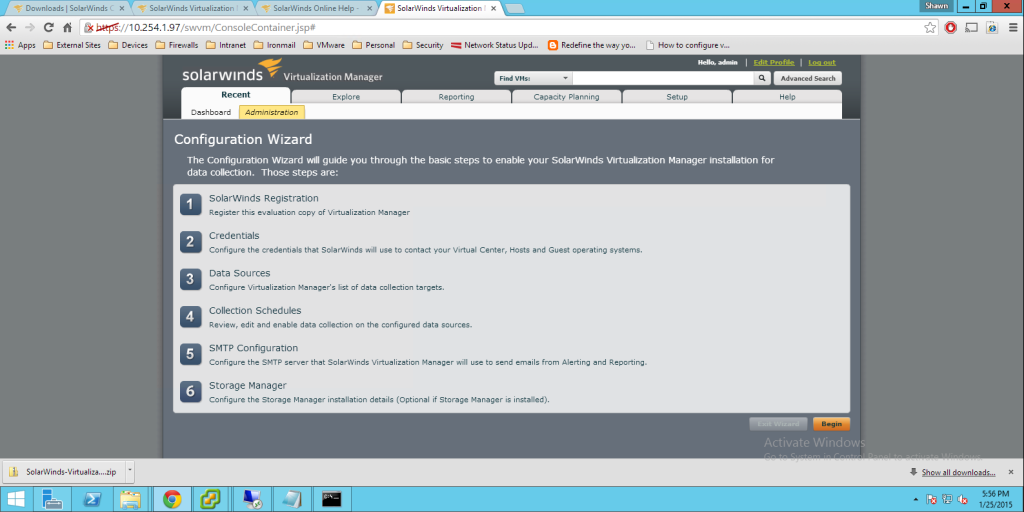
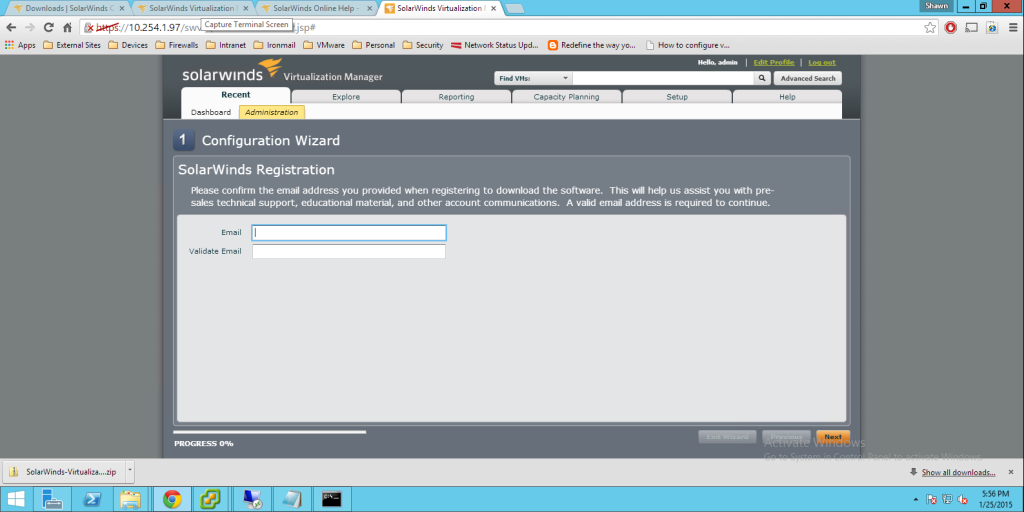
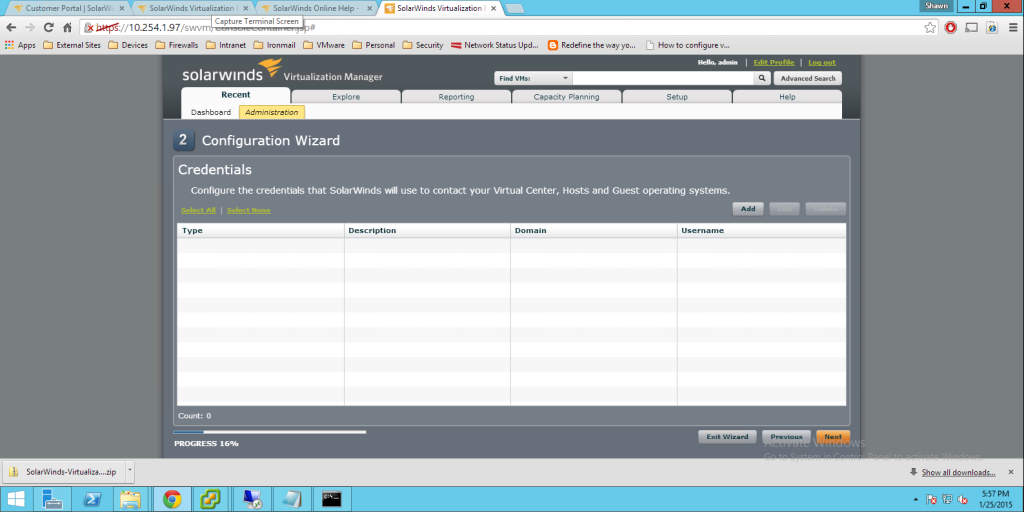
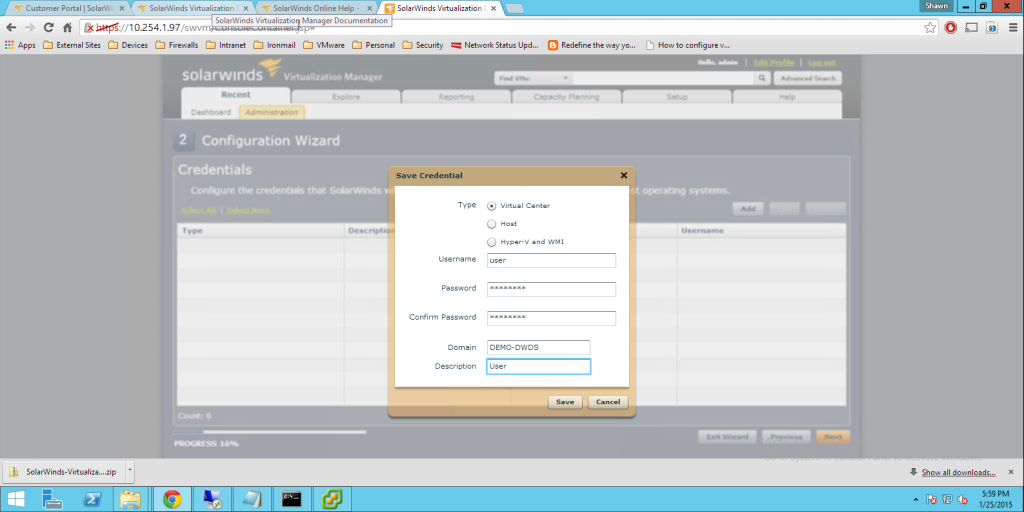
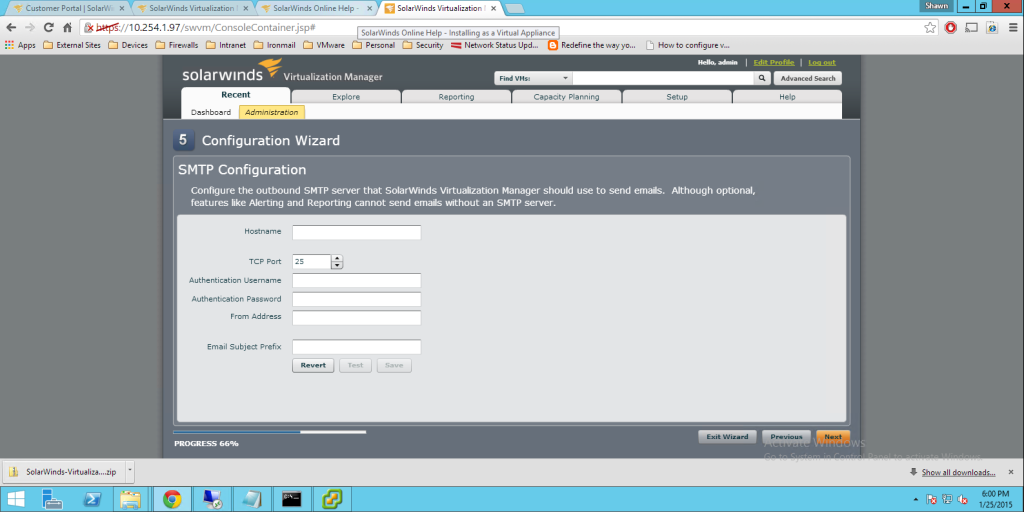
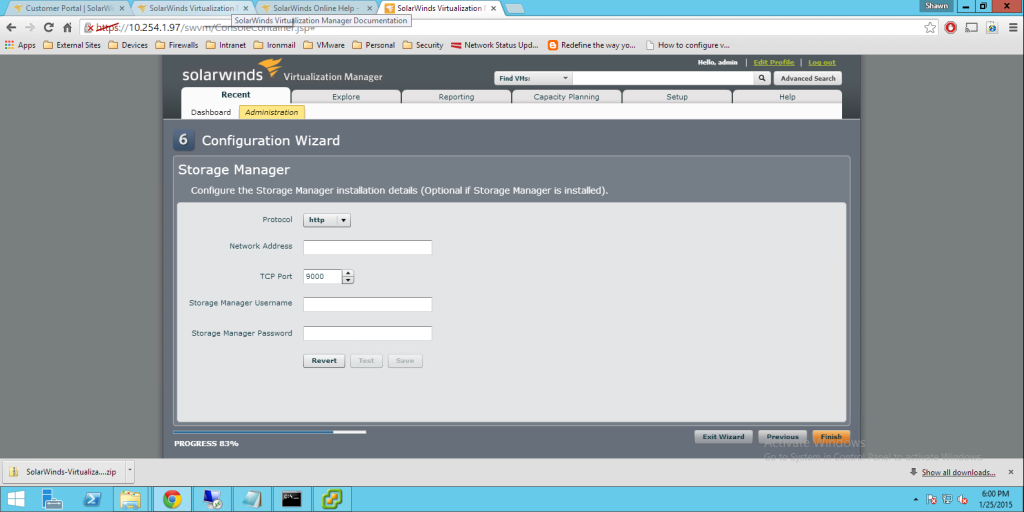
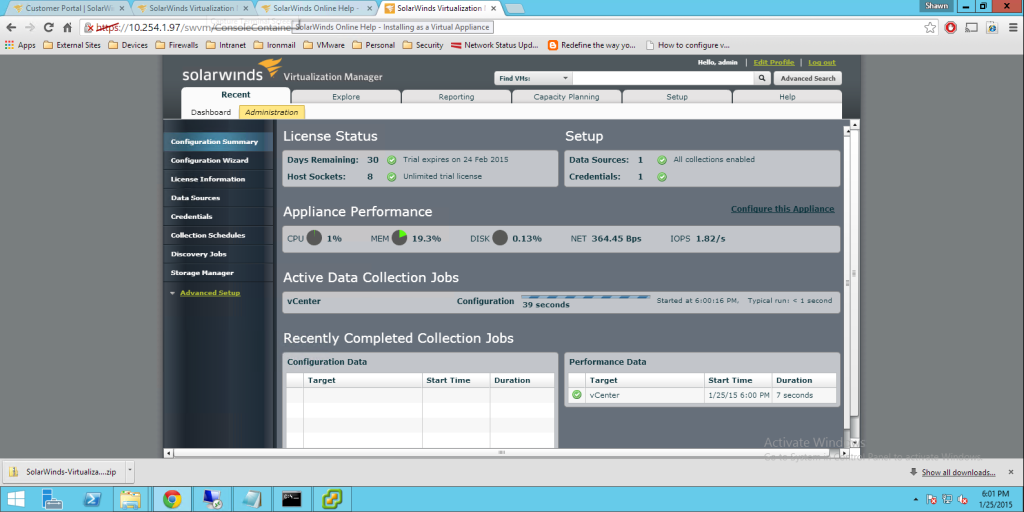
Today Announces the release of VMware’s vCenter largest release in VMware History. Note. These facts are pre release, thus I will update any changes if necessary, All Facts are direct From VMware.
vCenter Server Features – Enhanced Capabilities
|
Metric
|
Windows
|
Appliance
|
|
Hosts per VC
|
1,000
|
1,000
|
|
Powered-On VMs per VC
|
10,000
|
10,000
|
|
Hosts per Cluster
|
64
|
64
|
|
VMs per Cluster
|
8,000
|
8,000
|
|
Linked Mode
|
✔
|
✔
|
Platform Services Controller
Platform Services Controller includes takes it beyond just Single Sign-On. It groups:
- Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Licensing
- Certificate Authority
Linked Mode Comparison
|
vSphere 5.5
|
vSphere 6.0
|
|
|
Windows
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Appliance
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
Single Inventory View
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Single Inventory Search
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Replication Technology
|
Microsoft ADAM
|
Native
|
|
•Roles & Permissions
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
•Licenses
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
•Policies
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
•Tags
|
No
|
Yes
|
Certificate Lifecycle Management for vCenter and ESXi
VMware Certificate Authority (VMCA)
Provisions each ESXi host, each vCenter Server and vCenter Server service with certificates that are signed by VMCA
VMware Endpoint Certificate Service (VECS)
Stores and Certs and Private Keys for vCenter Services
vCenter Server 6.0 – VMCA
Root CA
- During installation, VMCA automatically creates a self-signed certificate
- This is a CA certificate, capable of issuing other certificates
- All solutions and endpoint certificates are created (and trusted) from this self-signed CA certificate
Issuer CA
- Can replace the default self-signed CA certificate created during installation
- Requires a CSR issued from VMCA to be used in an Enterprise/Commercial CA to generate a new Issuing Certificate
- Requires replacement of all issued default certificates after implementation
Certificate Replacement Options for vCenter Server
VMCA Default
- Default installed certificates
- Self-signed VMCA CA certificate as Root
- Possible to regenerate these on demand easily
VMCA Enterprise
- Replace VMCA CA certificates with a new CA certificate from the Enterprise PKI
- On removal of the old VMCA CA certificate, all old certificates must be regenerated
Custom
- Disable VMCA as CA
- Provision custom leaf certificates for each solution, user and endpoint
- More complicated, for highly security conscious customers
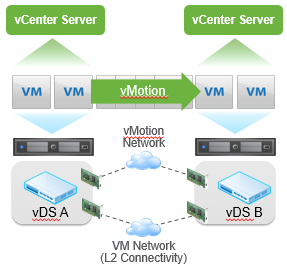
Cross vSwitch vMotion
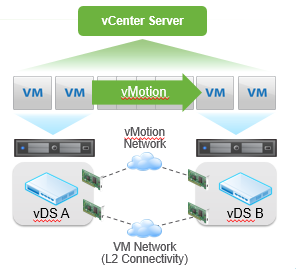
- Transparent operation to the guest OS
- Works across different types of virtual switches
- vSS to vSS
- vSS to vDS
- vDS to vDS
- Requires L2 network connectivity
- Does not change the IP of the VM
- Transfers vDS port metadata
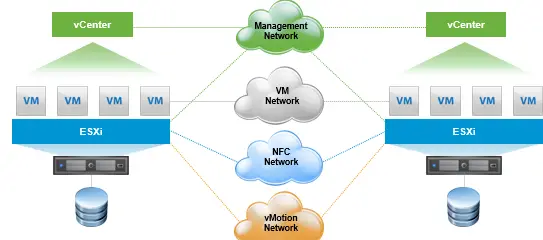
Cross vCenter vMotion
- Simultaneously changes
- Compute
- Storage
- Network
- vCenter
- vMotion without shared storage
- Increased scale
- Pool resources across vCenter servers
- Targeted topologies
- Local
- Metro
- Cross-continental
Requirements
- vCenter 6.0 and greater
- SSO Domain
- Same SSO domain to use the UI
- Different SSO domain possible if using API
- 250 Mbps network bandwidth per vMotion operation
- L2 network connectivity on VM portgroups
- IP addresses are not updated
Features
- VM UUID maintained across vCenter server instances
- Not the same as MoRef or BIOS UUID
- Data Preservation
- Events, Alarms, Tasks History
- HA/DRS Settings
- Affinity/Anti-Affinity Rules
- Automation level
- Start-up priority
- Host isolation response
- VM Resource Settings
- Shares
- Reservations
- Limits
- MAC Address of virtual NIC
- MAC Addresses preserved across vCenters
- Always unique within a vCenter
- Not reused when VM leaves vCenter
Long Distance vMotion
- Cross-continental distances – up to 100ms RTTs
- Maintain standard vMotion guarantees
- Does not require VVOLs
- Use Cases:
- Permanent migrations
- Disaster avoidance
- Multi-site load balancing
- Follow the sun
Increased vMotion Network Flexibility
- vMotion network will cross L3 boundaries
- vMotion can now use it’s own TCP/IP stack
Content Library Overview
- Simple content management
- VM templates
- vApps
- ISO images
- Scripts
- Store and manage content
- One central location to manage all content
- Beyond templates within vCenter
- Support for other file types
- Share content
- Store once, share many times
- Publish/Subscribe
- vCenter -> vCenter
- vCloud Director -> vCenter
- Consume content
- Deploy templates to a host or a cluster
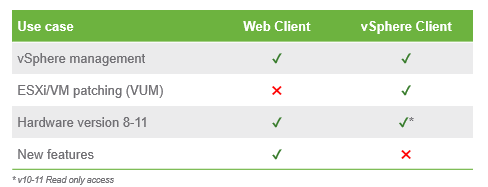
Client Overview and Web client Changes
Client Comparison
vSphere Client
- It’s still here
- Direct Access to hosts
- VUM remediation
- New features in vSphere 5.1 and newer are only available in the web client
- Added support for virtual hardware versions 10 and 11 *read only*
vSphere Web Client
- Performance
- Improved login time
- Faster right click menu load
- Faster performance charts
Usability
- Recent Tasks moved to bottom
- Flattened right click menus
- Deep lateral linking
- Major Performance Improvements
UI
- Screen by screen code optimization
- Login now 13x faster
- Right click menu now 4x faster
- Most tasks end to end are 50+% faster
- Performance charts
- Charts are available and usable in less then half the time
- VMRC integration
- Advanced virtual machine operations
- Usability Improvements
- Can get anywhere in one click
- Right click menu has been flattened
- Recent tasks are back at the bottom
- Dockable UI
vCenter Cluster Support
vCenter server is now supported to be ran in a Microsoft Cluster.
That’s all of the changes we were presented with from VMware. What a ton of changes, I will dig into these more soon.
Update: a post vSphere 6 – Clarifying the misinformation has been posted to clairify any changes that have or will happen between beta and this post. I did my best to validate that my information is correct.
Roger L